Notes abt Crypto Economics
Introduction
Market is the most thing I’ve been interested in the past few days, especially, the crypto currencies. This post is based on Tascha’s note. I have been following her work for a month now and she has some pretty critical insights about the crypto market that I miss.
Lesson 1. Crypto disrupts economic inequality
1 The magic of compounding
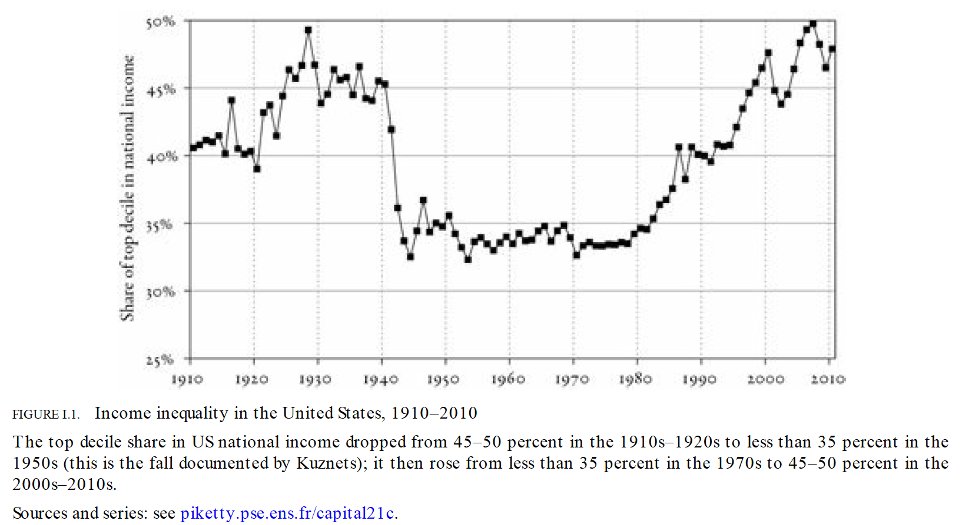
The current median net worth in US is 120k and the top 1% wealth club starts at 11 million. So the gap btw is 10.88 million. Let us assume both get 5% annual return the gap would be 17.72 million in 10 yrs which is a 60% increase. In order for the average person to be equal with the rich in 10 yrs, one needs a 50% annual return each year. Don’t forget that the rich person is still getting a 5% annual return. It does seem impossible to make this possible. However, fortunately, a tectonic shift of economic structure is happening that may occur once in three generations. The annual return of ethereum and bitcoin are both over 200% in past 5 and 10 years. But, it doesn’t mean that the riches do not know about the crypto. How does that change the inequality? This leads to the next reason.
2 The rich can buy more assets
Coming back to the assumption, the rich get half million dollars each year as 5% annual return which is enough for reinvesting and affording a good lifestyle. However, if you are just an average, you get 6000 dollars which is not even sufficient enough to pay the groceries. Luckily, the world is about to solve the ‘Global Asset Shortage’ problem. Global asset shortage is when asset supply has difficulited keeping up with the global demands. It has been uprising since the early 2000s because of three things. First, emerging market GDP is growing fast. Second, derivative asset classes like mortage-backed securities got destroyed in global financial crisis. Third, traditional asset classes like US treasuries are losing their social agreement. Perpetual monetary loosening of advanced economies with high indept damages the value of fiats. Gradually, the social agreement of these assets would start to turn fragile. Eventually, the demand for new asset classes will lead the crowd’s attention to cryptos due to its non geographical limitation of asset ownership. I think I can relate this to NFTs which is just rare pokemon cards that can be exchanged online without any geographical restrictions such as mailing fees.
Coming back to the main point, crypto creates new types of assets that are more attractive than the existing ones. Current crypto assets already serve as a new stores of values (e.g. NFT, bitcoin) and benefit from economic growth (e.g. staking, liquidity pools) and the entry barrier for each service is drastically lower. As crypto assets enter into our lives, it will help prevent price increase in physical assets like real estate. This does not change the paradigm of the inequality but it will reduce the price concentration toward residential assets.
3 The rich get higher returns
Unlike the first assumption, the rich and the average have huge annual return difference somewhat 10% vs 2%. Crypto is going to change pattern if we look over the history.
- 18th century capital: farm land
- 19th century capital: factories, machineas, government bonds
- 20th century capital: urban real estate, stocks
During the shift, the rich from old paradigm lose out because of their wealth is destroyed in value. Just like the many landowners suffered from major decline when agricultural export from the new continent flooded world market. In a result, there has been a major drop in wealth inequality of Britain since early 20th century. 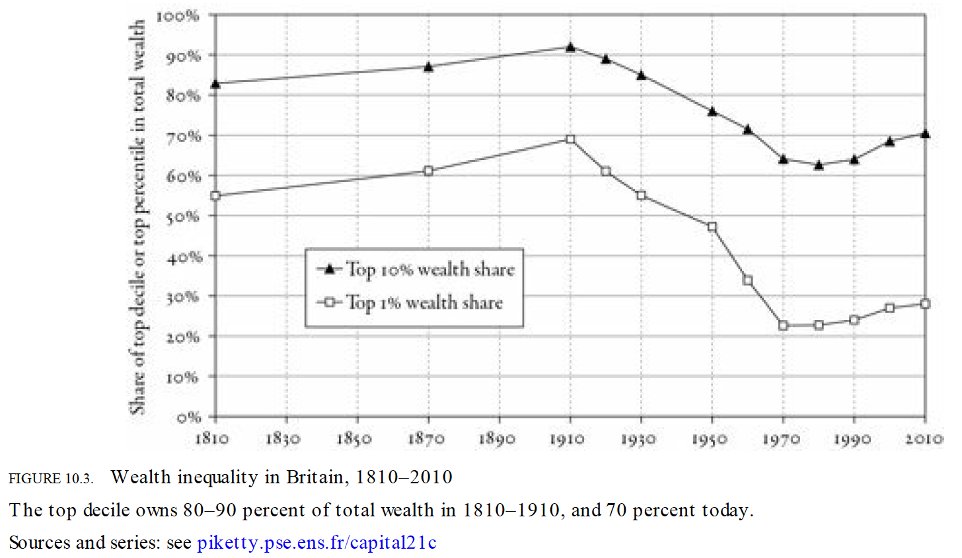
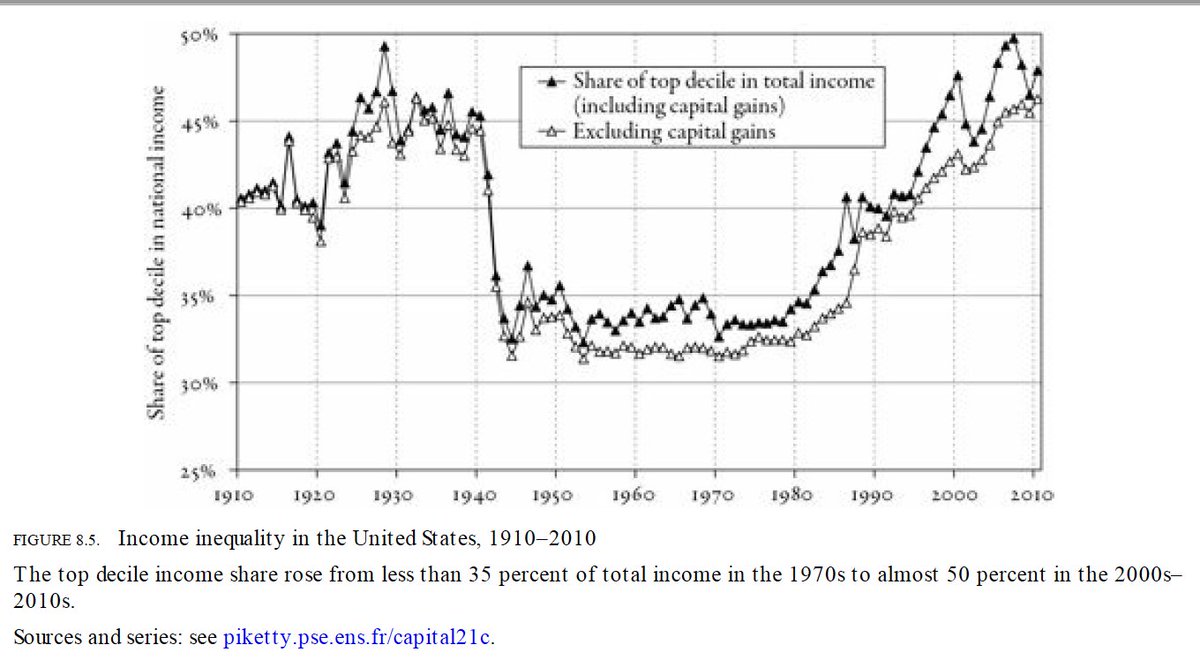
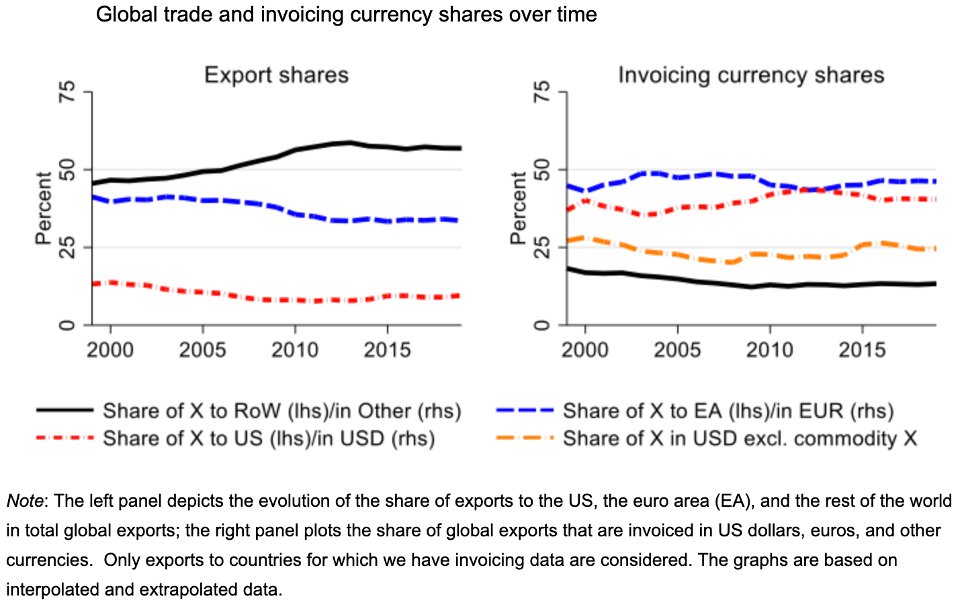
- 21st century capital: digital assets The rich, of course, will invest in crypto just like the landowners who started buying factories and machines. However, the generation accumulated wealth does not mean it comes with a vision. Totak global stock market cap is 120 trillion, real estate value 350 trillion, and the crypto market cap is 2 trillion. If crypto grows at the same pace as in the past 5 yrs for next 5-6 years, it will surpass global equity and real estate combined in market cap by 2027. However, it is very unlikely the pace will go on since there are going to be regulations such as Fed rate hikes. So, we will have to see how it goes.
Lesson 2. Layer-1 blockchain staking: the base layer of a new global financial paradigm
Something to think about; Ethereum = future risk-free asset
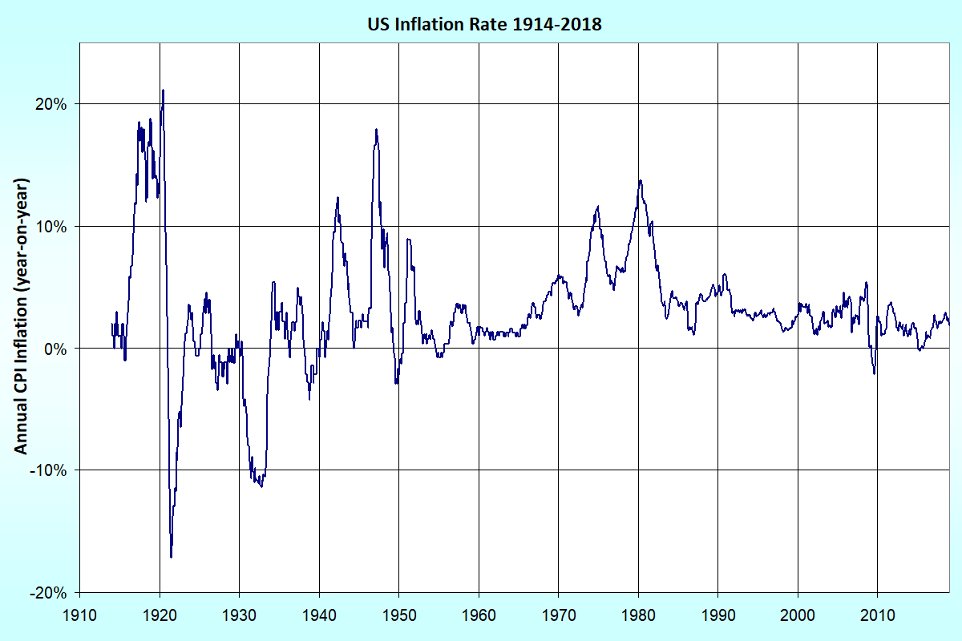
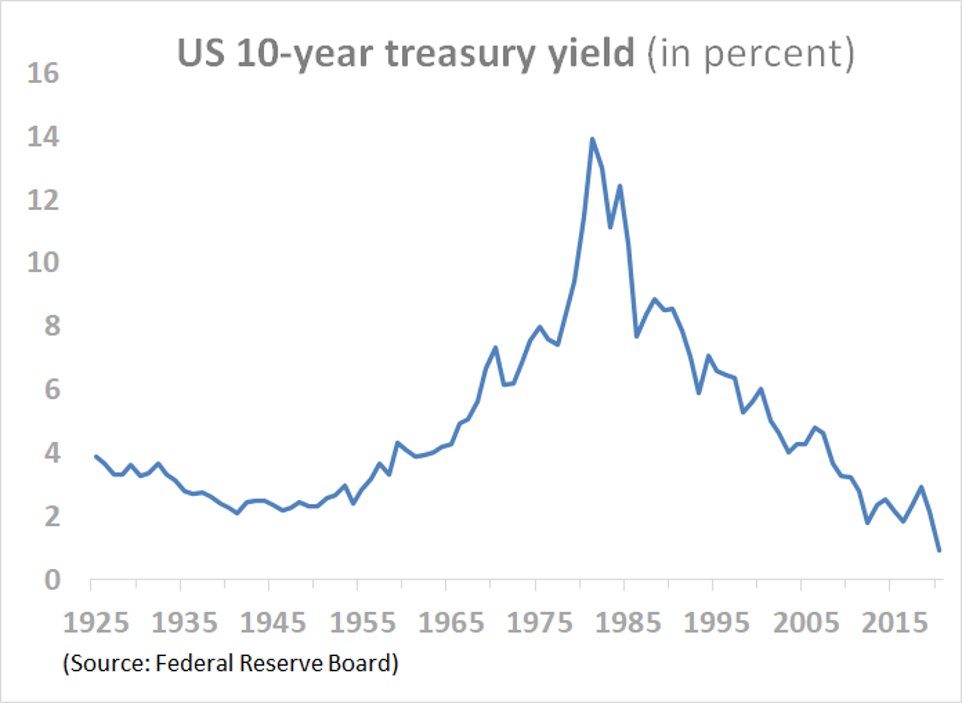
Can staked Ethereum or PoS act as the next global bond? Will it be the next US treasury? The biggest reason the US treasury have been indicated as the risk-free asset is because it is backed by tax incomes from the biggest economy in the world. If Ethereum becomes the world strongest PoS (Proof-of-Stake), the gas fees will operate as the tax incomes not from the biggest economy but the whole economy, the global GDP. There has been some momentum toward this direction recently, we can see that from staking cryptos. But where does the gas fees go? Once Eth switches to PoS, the gas incomes go to the stakers (validators). Bitcoin which is PoW, is impossible to play this role since miners compete for new blocks. In the long term, if Eth keeps its status as the dominant smart contract chain, and grows to more and more activites, over time the yield should track global real GDP (growth + inflation).
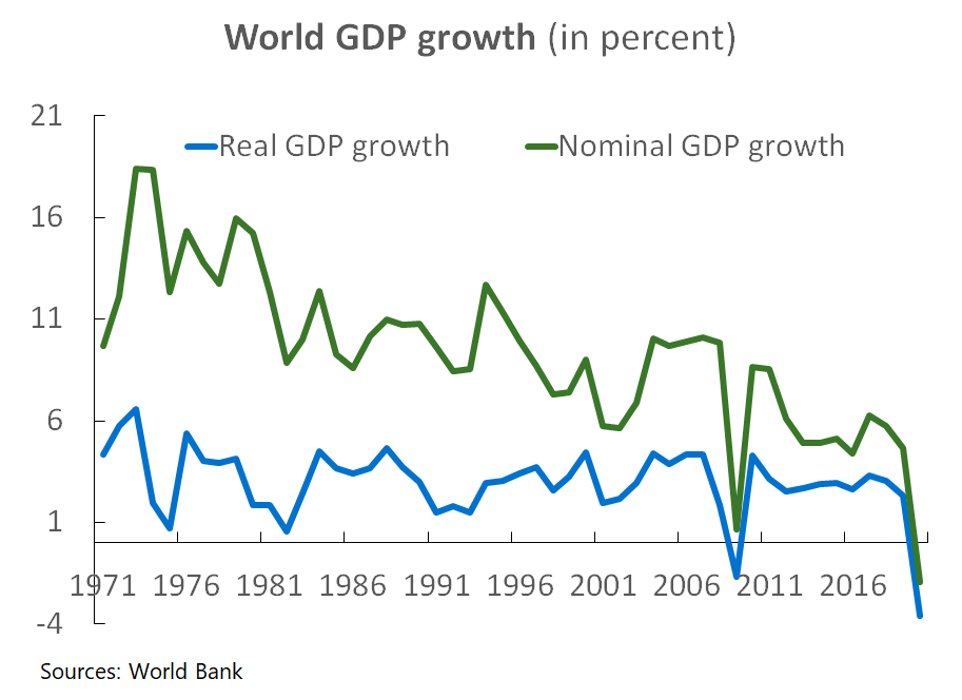
The US 10-year treasury yield in long run doesn’t seem so promising that it will overrun US real GDP completely. As you can see the charts below the world inflation is getting worse.
How about Bitcoin?
A money that can’t expand would crush the economy and put us all in poverty. We can’t print Bitcoin which will cause problems such as
- monetary tightening during economic crisis
- inflation volitality
- not enough bitcoins to go around
- global commerce and economy would shrink
Lesson 3. Defi: real financial innovation or speculative gold rush?
Potential momentum for deFi to surpass tradFi
- Low operating cost by design
Bank is an expensive business. Each branch in US costs 600k per year, an average bank has 20 branches which is 12 million a year. However, deFi app offers deposit/lending services (=banking) for 50-100k. The public blockchain works as a fuel so DeFi can run just like AWS provided millions of SaaS.
- High capital efficiency Bank is limited by the geographical size of the market and the fixed cost is high. For say, when the bank has a fixed cost of 100, they would have to sell 10 loans when each is 10. In a result, when there is a market doesn’t have the demand for the number, no bank would exist there. By contrast, the DeFi apps can move around the capital internationally wherever to a market that has higher demand.
- Co-op ownership model The stakers of the blockchians DeFi runs on are the “customers” who are providing the liquidity to the DeFi platform to get a share of the profit. In other words, the customers are able to earn incentives from keep using the platform which is not so much different from buying stocks of a bank of use. However, the banks’ profit is not transparent since they are allowed to do as they want.
Criticism: DeFi is not quite dencentralized
If any big whale like JP Morgan wants to take over DeFi apps like AAVE, it would be not much of a problem. This in case would be a monopoly of big whales just like banking. However, since DeFi entry barrier is so low, users will always have plenty of other options.
Lesson 4. DeFi: where do those yields come from?
6 Types of long-term yields
- Earning a platform token by using the product E.g. deFi version of “play to earn” a.k.a crypto gaming. It sounds promising, however, it is more of a wage than yields. It allows you to vote on project direction, but if you’re not a whale, your vote doesn’t mean a lot.
- Liquidity pools in AMMs (Automated market makers)
When you add tokens to a liquidity pool in AMMs like Uniswap, you earn a fee when people swap btw two tokens. Except when the two tokens price move in unison, you will earn yields.
- Lending stablescoins to HODLers who leverage long Some leverage investors would take crypto prices as up only, so if you lend some crypto to them, when the price are up, you are taking a small share of the gain. However, the pyramid might blow up like a bubble since there are a whole lot of new money coming in every day. But since, your yield is not tied to an individual project and is a stake in broader crypto ecosystem, the borrowers can take your loan to buy a variety of tokens.
- Receiving a platform token as dividend An example is Sushi Swap’s xSUSHI. Sushi takes a cut in swaps and other stuff on their platform. Holding xSUSHI provides liquidity for Sushi in exchange for a slice of their revenues.
- Lending to arbitragers Since the price margins for short-term arbitrages are not big, traders need to move larger amounts of capital to make it worthwhile. However, the deFi apps do not have this kind of capital so there are some demands for this type of loans. This is a relatively reliable yield since it does not depend on crypto prices going one direction. Additionally, the arbitragers have better risk control than most retails. In conclusion, we need to be careful when crypto becomes the beast in financial system. In current situation, there is always enough liquidity to push back up when the prices drop 80%. However, just like 2008 crisis, when all asset prices drop sharply, there is little liquidity anywhere to save any particular market.
Lesson 5. NFT: the democratization of asset creation
Asset: instruments to transfer ownership of value across time and space
Assets are ownerships that are priced based on how well it will carry out. Asset bubble is when you have more ownership than it needs to be preserved and transferred than asset instrument to do so which will result the token price to go up. The token price would not go up if when the supply of tokens keeps up the pace, but in reality, the expansion of asset at the pace of GDP growth is not so easy. Of course, there are other many possible causes to it, however, in the recent two decades, the major problems were perennial asset shortage. Global asset shortage is when asset supply has a hard time keeping up with global demand for value store, transfer and collateral. The causes are mentioned above. NFT will grow because it democratizes asset creation. NFT communities would run as a social agreement just like how bitcoin communities ran. Hopefully NFTs will be created in many form of digital assets just like how Youtube democratized film creation.
NFT: what makes tokenized assets better than physical ones
What is so special about token is that it only has the asset’s core function. It does not have the physical utility which in some cases we don’t ever use such as diamond rings. If a physical version of an asset is damaged or used, it loses its value. However, NFTs can be dispersed but still hold values. SoV (Store of Value) is always valid when it has a limited supply, long durability and social agreement. Additionally, a lot of physical assets have no liquid markets for them. You have to find an “expert” who can tell you how much they are worth, find a buyer and handle transferring. So, therefore, physical assets would only function as tools and the SoV role would be replaced by digital ones.
Lesson 6. Digitized fiat: the impact of a digital USD
America’s biggest export is the USD.